To use all functions of this page, please activate cookies in your browser.
my.chemeurope.com
With an accout for my.chemeurope.com you can always see everything at a glance – and you can configure your own website and individual newsletter.
- My watch list
- My saved searches
- My saved topics
- My newsletter
Isothermal–isobaric ensemble
The isothermal–isobaric ensemble (constant temperature and constant pressure ensemble) is a statistical mechanical ensemble that maintains constant temperature Additional recommended knowledgewhere There are several candidates for the normalization factor The characteristic state function of this ensemble is the Gibbs free energy, This thermodynamic potential is related to the Helmholtz free energy (logarithm of the canonical partition function), |
|||||||
| This article is licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License. It uses material from the Wikipedia article "Isothermal–isobaric_ensemble". A list of authors is available in Wikipedia. |


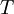 and constant pressure
and constant pressure 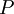 applied. It is also called the
applied. It is also called the 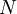 is also kept as a constant. This ensemble plays an important role in chemistry as chemical reactions are usually carried out under constant pressure condition. The partition function can be written as the weighted sum of the paritition function of
is also kept as a constant. This ensemble plays an important role in chemistry as chemical reactions are usually carried out under constant pressure condition. The partition function can be written as the weighted sum of the paritition function of 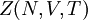 .
.
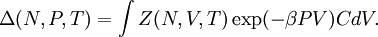



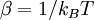 (
(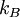 is Boltzmann factor), and
is Boltzmann factor), and 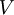 is volume of the system.
is volume of the system.
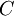 , e.g.,
, e.g., 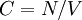 , or
, or 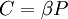 . These choices make the partition function a nondimensional quantity. The differences vanish in the thermodynamic limit, i.e., in the limit of infinite number of particles.
. These choices make the partition function a nondimensional quantity. The differences vanish in the thermodynamic limit, i.e., in the limit of infinite number of particles.
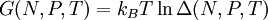
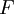 , in the following way:
, in the following way: