Freshmen-level chemistry solves the solubility mystery of graphene oxide films
Common contaminant found responsible for the material's stability in water
A Northwestern University-led team recently found the answer to a mysterious question that has puzzled the materials science community for years - and it came in the form of some surprisingly basic chemistry.
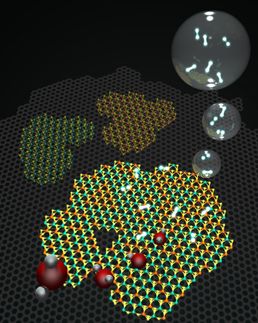
Like many scientists, Jiaxing Huang did not understand why graphene oxide (GO) films were highly stable in water. When submerged, the individual GO sheets become negatively charged and repel each other, which should cause membrane to disintegrate. But earlier papers noted that instead of disintegrating, the films stabilized.
"It doesn't make any sense," said Huang, associate professor of materials science and engineering at the McCormick School of Engineering. "Many scientists have been very puzzled by this."
Graphene oxide, a product of graphite oxidation, is often used to make graphene, a single-atom-layer thick sheet of carbon that is remarkably strong, lightweight, and has high potential in electronics and energy storage. Within the past three years, however, more scientists have become interested in GO itself, partially because of its potential for molecular separation applications.
After studying the material for many years, Huang realized that the secret of GO's mysterious insolubility was the unintentional introduction of a common contaminant. To make a GO film, many scientists pass the acidic dispersion of individual sheets through porous anodized aluminum oxide filter discs, which are popularly used for preparing membranes of many nanomaterials. Huang's team found that during filtration, the aluminum filter discs corrode in acidic water to release a significant number of aluminum ions, Al3+. The positively charged ion bonds with the negatively charged GO sheets to stabilize the resulting membranes.
"We have solved the puzzle using essentially freshman-level inorganic chemistry," Huang said. "Now we know that graphene oxide films are indeed soluble in water. It's just a matter of sample purity."
Other multivalent metal ions, such as manganese, which is a byproduct from the synthesis of GO, can also crosslink the sheets.
Original publication
"On the origin of stability of graphene-oxide membranes in water."; Nature Chemistry.
Most read news
Original publication
"On the origin of stability of graphene-oxide membranes in water."; Nature Chemistry.
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
From now on, don't miss a thing: Our newsletter for the chemical industry, analytics, lab technology and process engineering brings you up to date every Tuesday and Thursday. The latest industry news, product highlights and innovations - compact and easy to understand in your inbox. Researched by us so you don't have to.