Atomically thin sensor detects harmful air pollution in the home
Scientists from the University of Southampton, in partnership with the Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (JAIST), have developed a graphene-based sensor and switch that can detect harmful air pollution in the home with very low power consumption.
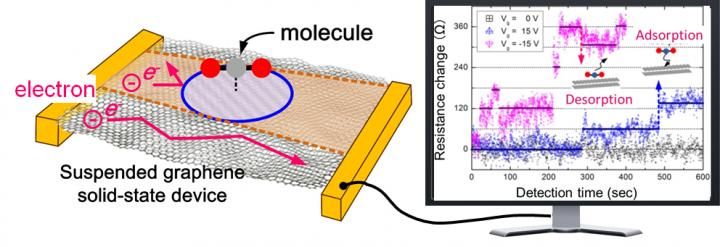
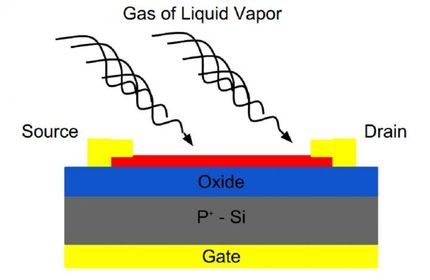
A diagram of a graphene single molecular sensor (left) and the observed signal showing successful detection of single CO2 molecule adsorption / desorption events.
University of Southampton
The sensor detects individual CO2 molecules and volatile organic compound (VOC) gas molecules found in building and interior materials, furniture and even household goods, which adversely affect our living in modern houses with good insulation.
These harmful chemical gases have low concentrations of ppb (parts per billion) levels and are extremely difficult to detect with current environmental sensor technology, which can only detect concentrations of parts per million (ppm).
In recent years, there has been an increase in health problems due to air pollution in personal living spaces, known as sick building syndrome (SBS), along with other conditions such as sick car and sick school syndromes.
The research group, led by Professor Hiroshi Mizuta, who holds a joint appointment at the University of Southampton and JAIST, and Dr Jian Sun and Assistant Professor Manoharan Muruganathan of JAIST, developed the sensor to detect individual CO2 molecules adsorbed (the bond of molecules from a gas to a surface) onto the suspended graphene (single atomic sheet of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb-like hexagonal crystal lattice structure) one by one by applying an electric field across the structure.
By monitoring the electrical resistance of the graphene beam, the adsorption and desorption (whereby a substance is released from or through a surface) processes of individual CO2 molecules onto the graphene were detected as 'quantised' changes in resistance (step-wise increase or decrease in resistance). In the study, published in Science Advances a small volume of CO2 gas (equivalent to a concentration of approximately 30 ppb) was released and the detection time was only a few minutes.
Professor Mizuta said: "In contrast to the commercially available environmental monitoring tools, this extreme sensing technology enables us to realise significant miniaturisation, resulting in weight and cost reduction in addition to the remarkable improvement in the detection limit from the ppm levels to the ppb levels."
Research group members, Dr Harold Chong from Southampton and Dr Marek Schmidt and Dr Jian Sun of JAIST, have also recently developed graphene-based switches using a uniquely thin film developed at the University of Southampton.
The switches, which require remarkably low voltages (below three volts), can be used to power electronic components on demand, greatly improving the battery lifetime of personal electronic devices.
Professor Mizuta and the research group are now aiming to bring the two technologies together to create ultra-low-power environmental sensor systems that can detect single molecules.
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Sensor technology
Sensor technology has revolutionized the chemical industry by providing accurate, timely and reliable data across a wide range of processes. From monitoring critical parameters in production lines to early detection of potential malfunctions or hazards, sensors are the silent sentinels that ensure quality, efficiency and safety.

Topic world Sensor technology
Sensor technology has revolutionized the chemical industry by providing accurate, timely and reliable data across a wide range of processes. From monitoring critical parameters in production lines to early detection of potential malfunctions or hazards, sensors are the silent sentinels that ensure quality, efficiency and safety.