To use all functions of this page, please activate cookies in your browser.
my.chemeurope.com
With an accout for my.chemeurope.com you can always see everything at a glance – and you can configure your own website and individual newsletter.
- My watch list
- My saved searches
- My saved topics
- My newsletter
Gibbs measureIn statistical mechanics, a Gibbs measure is a probability measure that relates the probabilities of the various possible states of a system to the energies associated to them. Although the precise definition requires some care (particularly in the case of infinite systems), the main characteristic of a Gibbs measure is that the probability of the system assuming a given state ω with associated energy E(ω) at inverse temperature β is proportional to Product highlightFormal definitionThe definition of a Gibbs random field on a lattice requires some terminology:
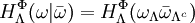 , ,
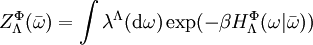 . .
A probability measure μ on 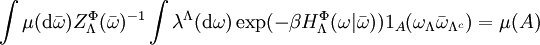 , ,
An exampleTo help understand the above definitions, here are the corresponding quantities in the important example of the Ising model with nearest-neighbour interactions (coupling constant J) and a magnetic field (h), on
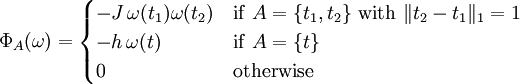 References
|
| This article is licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License. It uses material from the Wikipedia article "Gibbs_measure". A list of authors is available in Wikipedia. |


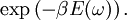



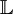 .
.
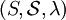 .
.
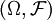 , where
, where 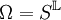 and
and 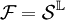 .
.
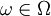 and a subset
and a subset 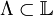 , the restriction of
, the restriction of 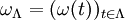 . If
. If 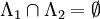 and
and 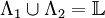 , then the configuration
, then the configuration 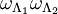 is the configuration whose restrictions to
is the configuration whose restrictions to 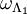 and
and 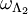 , respectively.
, respectively.
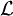 of all finite subsets of
of all finite subsets of 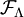 is the
is the 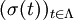 , where
, where 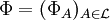 of functions
of functions 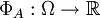 such that
such that
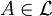 ,
, 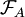 -measurable.
-measurable.
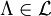 and
and 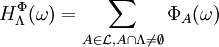 exists.
exists.
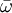 , for the potential
, for the potential 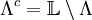 .
.
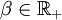 (for the potential
(for the potential 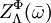 is finite for all
is finite for all 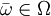 and
and 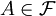 and
and 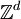 :
:
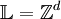 .
.


