To use all functions of this page, please activate cookies in your browser.
my.chemeurope.com
With an accout for my.chemeurope.com you can always see everything at a glance – and you can configure your own website and individual newsletter.
- My watch list
- My saved searches
- My saved topics
- My newsletter
Solenoidal vector fieldIn vector calculus a solenoidal vector field is a vector field v with divergence zero: Product highlightThis condition is satisfied whenever v has a vector potential, because if then The converse also holds: for any solenoidal v there exists a vector potential A such that The divergence theorem, gives the equivalent integral definition of a solenoidal field; namely that for any closed surface S, the net total flux through the surface must be zero:
where Examples
|
| This article is licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License. It uses material from the Wikipedia article "Solenoidal_vector_field". A list of authors is available in Wikipedia. |
- Category:Semiconductor_analysis
- Lipinski's_Rule_of_Five
- CSIC presents its prototype vanadium battery for large-scale electrical energy storage - 10 kW redox flow demonstrator paves the way for a 50 kW flow battery
- DNA
- Gold shines through properties of nano biosensors - Fluorescence in ligand-protected gold nanoclusters is an intrinsic property of the gold particles themselves


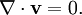




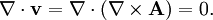
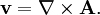 (Strictly speaking, this holds only subject to certain technical conditions on v, see Helmholtz decomposition.)
(Strictly speaking, this holds only subject to certain technical conditions on v, see Helmholtz decomposition.)
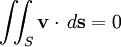 ,
,
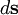 is the outward normal to each surface element.
is the outward normal to each surface element.


