To use all functions of this page, please activate cookies in your browser.
my.chemeurope.com
With an accout for my.chemeurope.com you can always see everything at a glance – and you can configure your own website and individual newsletter.
- My watch list
- My saved searches
- My saved topics
- My newsletter
Vector bosonA vector boson is a boson with spin equal to one unit of Product highlightThere also exist composite particles that are vector bosons, such as the vector mesons, made of a quark and antiquark with a total angular momentum of one unit. ExplanationThe name vector boson arises from quantum field theory. The component of such a particle's spin along any axis will always be measured to have one of three values: See also |
| This article is licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License. It uses material from the Wikipedia article "Vector_boson". A list of authors is available in Wikipedia. |
- Phosphorus
- TOC & Water Analysis | TOC analysers | Elementar Analysensysteme
- Resonance_(chemistry)
- A better device to detect ultraviolet light - New type of photodiode, described in the journal Applied Physics Letters, shows promise for space-based communication and monitoring ozone depletion
- Glycocalyx


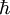 (Planck's constant divided by
(Planck's constant divided by 


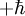 , 0, or
, 0, or 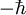 (this is, at least, true for massive vector bosons; the situation is a bit different for massless particles such as the photon, for reasons beyond the scope of this article). The space of spin states therefore has three degrees of freedom, the same as the number of components of a mathematical vector in three-dimensional space. Quantum superpositions of these states can be taken such that they transform under rotations just like the spatial components of a rotating vector. If the vector boson is taken to be the quantum of a field, the field is a vector field, hence the name.
(this is, at least, true for massive vector bosons; the situation is a bit different for massless particles such as the photon, for reasons beyond the scope of this article). The space of spin states therefore has three degrees of freedom, the same as the number of components of a mathematical vector in three-dimensional space. Quantum superpositions of these states can be taken such that they transform under rotations just like the spatial components of a rotating vector. If the vector boson is taken to be the quantum of a field, the field is a vector field, hence the name.


