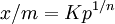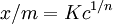To use all functions of this page, please activate cookies in your browser.
my.chemeurope.com
With an accout for my.chemeurope.com you can always see everything at a glance – and you can configure your own website and individual newsletter.
- My watch list
- My saved searches
- My saved topics
- My newsletter
Freundlich equationThe Freundlich Adsorption Isotherm is an adsorption isotherm, which is a curve relating the concentration of a solute on the surface of an adsorbent, to the concentration of the solute in the liquid with which it is in contact. Product highlightThe Freundlich Adsorption Isotherm is mathematically expressed as or where
K and 1/n are constants for a given adsorbate and adsorbent at a particular temperature.
The Langmuir adsorption isotherm describes quantitatively the build up of a layer of molecules on an adsorbent surface as a function of the concentration of the adsorbed material in the liquid in which it is in contact. In a modified form it can also describe a bi-layer deposition. The shape of the isotherm (assuming the (x) axis represents the concentration of adsorbing material in the contacting liquid) is a gradual positive curve that flattens to a constant value. It often represents an initial surface adsorption followed by a condensation effect resulting from extremely strong solute-solute interaction. In chromatography the Freundlich isotherm is not common, most adsorption processes are best described by the Langmuir isotherm. |
| This article is licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License. It uses material from the Wikipedia article "Freundlich_equation". A list of authors is available in Wikipedia. |