To use all functions of this page, please activate cookies in your browser.
my.chemeurope.com
With an accout for my.chemeurope.com you can always see everything at a glance – and you can configure your own website and individual newsletter.
- My watch list
- My saved searches
- My saved topics
- My newsletter
Reynolds decompositionIn fluid dynamics and the theory of turbulence, Reynolds decomposition is a mathematical
technique to separate the average and fluctuating parts of a quantity.
For example, for a quantity Product highlightwhere This allows us to simplify the Navier-Stokes equations by substituting in the sum of the steady component and perturbations to the velocity profile and taking the mean value. The resulting equation contains a nonlinear term known as the Reynolds stresses which gives rise to turbulence. See also |
| This article is licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License. It uses material from the Wikipedia article "Reynolds_decomposition". A list of authors is available in Wikipedia. |


 the decomposition woud be
the decomposition woud be
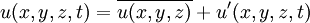



 denotes the time average of
denotes the time average of  (often called the steady component), and
(often called the steady component), and
 the fluctuating part (or perturbations). The perturbations are defined such that their time average equals zero.
the fluctuating part (or perturbations). The perturbations are defined such that their time average equals zero.


