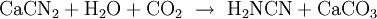To use all functions of this page, please activate cookies in your browser.
my.chemeurope.com
With an accout for my.chemeurope.com you can always see everything at a glance – and you can configure your own website and individual newsletter.
- My watch list
- My saved searches
- My saved topics
- My newsletter
Cyanamide
Cyanamide (CN2H2) is an amide of cyanogen, a white, crystalline compound. The term can also refer to a salt of this compound, having one or both of the hydrogen atoms replaced by another element or radical, such as in the most common case of calcium cyanamide (CaCN2), a compound used as a fertilizer and as a source of other compounds of nitrogen. Product highlight
ChemistryCyanamide can be prepared by hydrolysis of calcium cyanamide in presence of carbon dioxide by Frank-Caro process: UsesSince mid-1960s, there have been developed procedures to produce stabilized for industry use. Cyanamide is used as a plant growth modulator and has many uses in chemical industry. Safety risksAqueous solutions of cyanamide with high concentration may undergo explosive polymerisation when heated. Stability of its solution can be increased by addition of a dicarboxylic acid such as adipic acid.[1] References
Categories: Functional groups | Amides | Cyanamides | Inorganic carbon compounds | Nitrogen compounds |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This article is licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License. It uses material from the Wikipedia article "Cyanamide". A list of authors is available in Wikipedia. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||