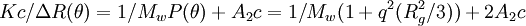To use all functions of this page, please activate cookies in your browser.
my.chemeurope.com
With an accout for my.chemeurope.com you can always see everything at a glance – and you can configure your own website and individual newsletter.
- My watch list
- My saved searches
- My saved topics
- My newsletter
Static light scatteringStatic light scattering is a technique in physical chemistry that uses the intensity traces at a number of angles to derive information about the radius of gyration There are typically a number of analyses developed to analyze the scattering of particles in solution to derive the above named physical characteristics of particles. A simple static light scattering experiment entails the average intensity of the sample that is corrected for the scattering of the solvent will yield the Rayleigh ratio,
One must note that although data analysis can be performed without a so-called material constant
where
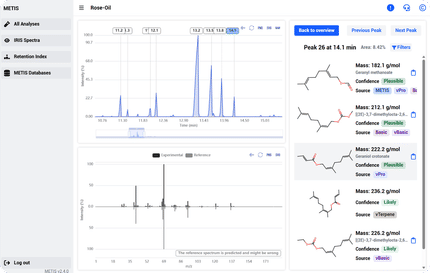
Product highlight
Data AnalysesGuinier plotThe scattered intensity can be plotted as a function of the angle to give information on the
Kratky plotThe Kratky plot is typically used to analyze the conformation of proteins, but can be used to analyze the random walk model of polymers. A Kratky plot can be made by plotting
Debye plotThis method is used to derive the molecular mass and 2nd virial coefficient,
Zimm plotFor polymers and polymer complexes which are of a monodisperse nature One must note that if the material constant
References1. A. Einstein, Ann. Phys. 33 (1910), 1275 2. C.V. Raman, Indian J. Phys. 2 (1927), 1 3. P.Debye, J. Appl. Phys. 15 (1944), 338 4. B.H. Zimm, J. Chem. Phys 13 (1945), 141 5. B.H. Zimm, J. Chem. Phys 16 (1948), 1093 See also
Categories: Polymer chemistry | Polymer physics | Physical chemistry |
|
| This article is licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License. It uses material from the Wikipedia article "Static_light_scattering". A list of authors is available in Wikipedia. |


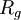 ,
, 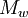 of the
of the 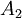 , for example,
, for example, 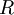 as a function of the angle or the wave vector
as a function of the angle or the wave vector 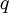 as follows:
as follows:
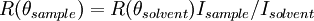
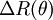 between the sample and solvent:
between the sample and solvent:
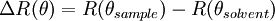
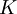 defined below, the inclusion of this constant can lead to the calculation of other physical parameters of the system.
defined below, the inclusion of this constant can lead to the calculation of other physical parameters of the system.
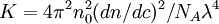
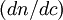 is the refractive index increment,
is the refractive index increment, 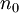 is the refractive index of the solvent,
is the refractive index of the solvent, 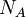 is
is 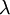 is the wavelength of the laser light reaching the detector. This equation is for linearly polarized light like the one from a
is the wavelength of the laser light reaching the detector. This equation is for linearly polarized light like the one from a 

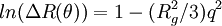
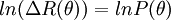 also known as the form factor with
also known as the form factor with 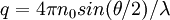 . Hence a plot of the corrected Rayleigh ratio,
. Hence a plot of the corrected Rayleigh ratio,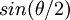 or
or 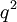 will yield a slope
will yield a slope 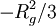 . However, this approximation is only true for
. However, this approximation is only true for 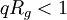 . Note that for a Guinier plot, the value of dn/dc and the concentration is not needed.
. Note that for a Guinier plot, the value of dn/dc and the concentration is not needed.
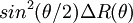 versus
versus 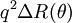 versus
versus 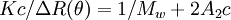
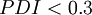 as determined by
as determined by