Layering
Layering – a High Quality and Cost Efficient Alternative to Spray Drying
IPC Process-Center GmbH & Co. KG






Refine Your Raw Materials to Homogenous, Stable and Safe Pellets
Layering is a term used for techniques applying a single layer or multiple layers of a substance onto a substrate .
For the upgrading of granular raw materials at IPC the layering process is performed in a Glatt® fluid bed equipment. Disperse raw material is applied onto a granular carrier material. The layering material usually is a valuable ingredient which by itself possesses unfavorable physical properties for the downstream processing, storage or final usage. Whereas the carrier material used as a neutral filling substance exhibits excellent handling properties.
Controlled Product Properties and Accurate Dosing of the Active
In product development, the selection of an appropriate carrier is important because the carrier material effectively determines the granulometric properties of the target formulation. Depending on the aimed application, parameters like bulk density, flowability, tensile strength and abrasion resistance may also be of interest in addition to the distribution of particle shape and size. Chemical interactions or unintended side effects can thus be prevented from occurring during the final use.
In contrast to spray drying, layering allows you to apply a high proportion of the high-value raw material to an affordable inert carrier, leaving you without the disadvantages of the valuable substance’s original properties but with the advantages of the carrier. In this way we convert scarcely free-flowing raw materials into easy-to-dose, compact and uniform granules with a defined surface structure.
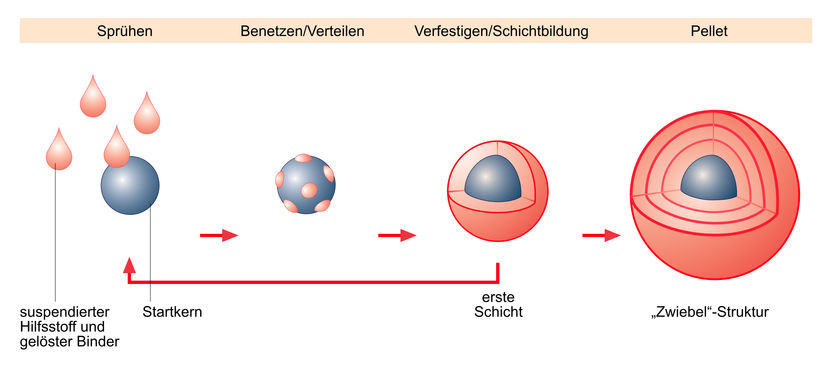
There are two techniques: powder layering and suspension layering. In the powder layering process, the active substance is a powder which is applied to a neutral carrier core by simultaneous wetting with a binder solution. The corresponding method is the rotor technology.
If the valuable or active substance is present in liquid form (as suspension, emulsion or solution), we use suspension layering. Technologically, the process is best performed in a fluidized bed apparatus. Neutral carriers (also known as starter pellets), with a grain size of typically between 100 and 1000 µm, are introduced into the fluidized bed system. The suspension that contains the valuable material is sprayed onto the carrier material, often by pneumatic two-substance nozzles. Fine liquid droplets spread over the surface of the carrier material, forming a liquid film. This film is immediately dried by heated process gas, leaving a uniform layer around the starter core. The growth of the layer can be flexibly adjusted: it is halted when the pellet reaches the desired value. This process is therefore ideal for producing a standardized product with a narrowly specified amount of the valuable substance. Precise control of the applied quantity makes it possible to level natural fluctuations of the raw material’s active content.
The Gentle Way of Drying
The process conditions are extremely gentle in terms of physical stress; hence the technology is particularly interesting for temperature-sensitive substances. Suspension layering is therefore frequently used for producing solid, enzyme-containing formulations. We are able to creates stable, dust-free and easy-to-dose granules from liquid enzyme suspensions, where spray drying tends to create dusty products with safety issues.
Similarly, suspension layering can granulate many other high-value ingredients used in the chemical and pharmaceutical industry, such as fermenter broths, vitamins, plant extracts, cosmetic ingredients, aromas, catalysts and adsorbents.
The Advantages of Pelleting Using Layering Techniques
- Homogeneous pellets
- Ease to dose
- Low hygroscopicity
- Dense, even and abrasion-resistant surfaces
- Narrow grain size distribution
- Exact control of active substance content
- Ideal for a wide range of applications in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries

1
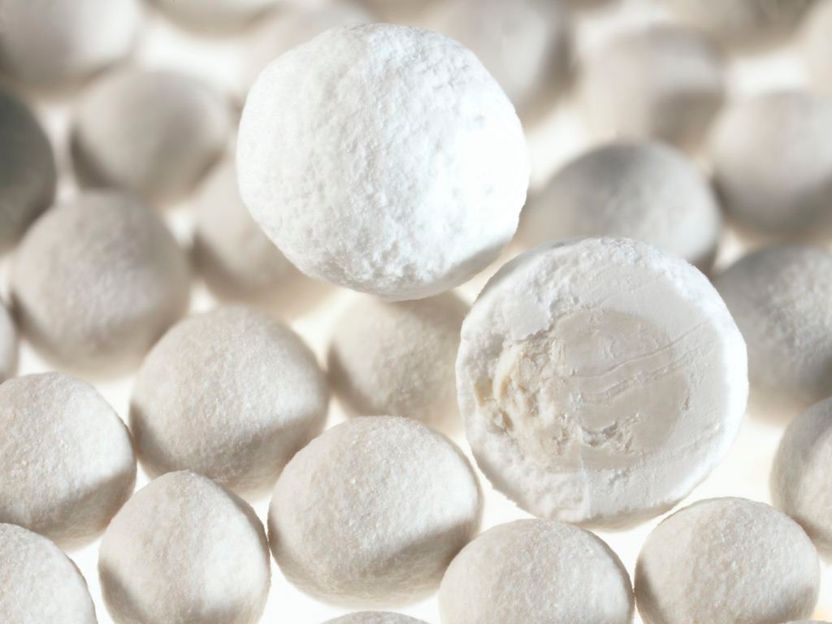
Close-up image of an amino acid pellet

2
The principle behind suspension layering

3
Close-up image of an adsorbent on an inert carrier

4
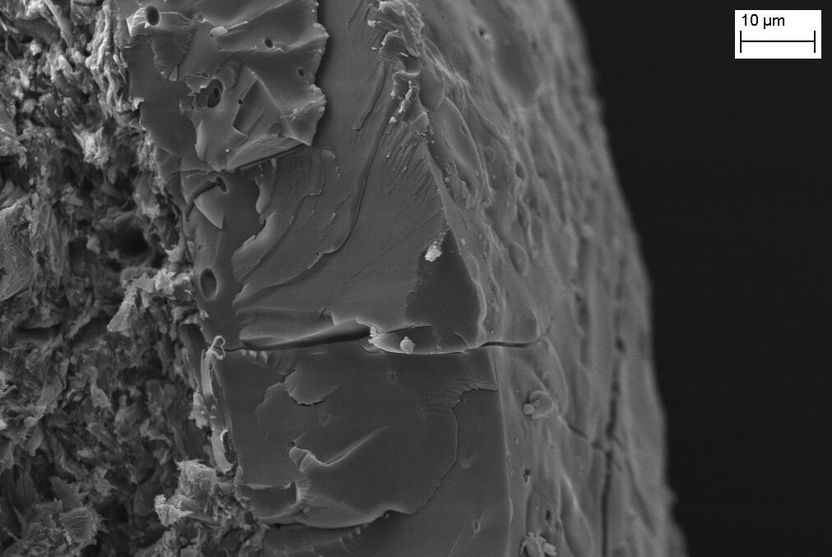
SEM image of a layer of dried fermenter broth

5
Close-up images of multilayer pellets
Request information about Layering now

Layering
Layering – a High Quality and Cost Efficient Alternative to Spray Drying




