Nanoparticle Assembly Enters the Fast Lane
Method borrows instructions from molecular code of life
The speed of nanoparticle assembly can be accelerated with the assistance of the molecule that carries life's genetic instructions, DNA, a team of researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory recently found. nanoparticles could potentially be used for more efficient energy generation and data storage, as well as improved methods for diagnosing and treating disease. Learning how to control and tailor the assembly of these miniscule particles into larger functional systems remains a major challenge for scientists. The Brookhaven results, published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, are a step in that direction.
"Understanding how to self-assemble these types of nanomaterials has applications in all areas of nanotechnology, from optics to electronics to magnetic materials," said the study's lead author Mathew Maye, a Brookhaven chemist. Maye is part of a team of interdisciplinary scientists from Brookhaven's new Center for Functional Nanomaterials (CFN) and the biology department. The researchers found a way to control the assembly of gold nanoparticles using rigid, double-stranded DNA. Their technique takes advantage of this molecule's natural tendency to pair up components called bases, known by the code letters A, T, G and C.
"In biology, DNA is mainly an informational material, while in nanoscience, DNA is an excellent structural material due to its natural ability to self-assemble according to well-specified programmable rules," said Oleg Gang, the Brookhaven physicist who leads the research team. "Using biological materials such as DNA, we are developing approaches to control the assembly of inorganic nano-objects. However, in order to really turn this attractive approach into nanotechnology, we have to understand the complexity of interaction in such hybrid systems."
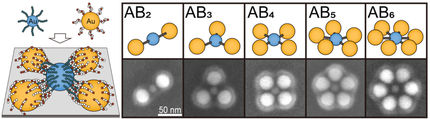
The synthetic DNA used in the laboratory is capped onto individual gold nanoparticles and customized to recognize and bind to complementary DNA located on other particles. This process forms clusters, or aggregates, of gold particles.
"It's really by design," Maye said. "We can sit down with a piece of paper, write out a DNA sequence, and control how these nanoparticles will assemble."
One limitation to the assembly process is the use of single-stranded DNA, which can bend backward and attach to the particle's gold surface instead of binding with surrounding nanoparticles. This flexibility, along with the existence of multiple forms of single-stranded DNA, can greatly slow the assembly process. In the Brookhaven study, researchers introduced partially rigid, double-stranded DNA, which forces interacting linker segments of DNA to extend away from the gold surface, allowing for more efficient assembly.
"By using properties of DNA, we can increase assembly kinetics, or speed, by relatively simple means without a lot of synthetic steps," Maye said.
The research team probed the synthesized and assembled nanosystems with multiple imaging techniques, using beams of light and electrons as well as high-intensity x-rays at Brookhaven's National Synchrotron Light Source. The scientists look to further improve the controllability of the system, focusing next on the size of the nanoparticle clusters.
Most read news
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you

NANOPHOX CS by Sympatec
Particle size analysis in the nano range: Analyzing high concentrations with ease
Reliable results without time-consuming sample preparation

Eclipse by Wyatt Technology
FFF-MALS system for separation and characterization of macromolecules and nanoparticles
The latest and most innovative FFF system designed for highest usability, robustness and data quality

DynaPro Plate Reader III by Wyatt Technology
Screening of biopharmaceuticals and proteins with high-throughput dynamic light scattering (DLS)
Efficiently characterize your sample quality and stability from lead discovery to quality control

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.