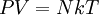To use all functions of this page, please activate cookies in your browser.
my.chemeurope.com
With an accout for my.chemeurope.com you can always see everything at a glance – and you can configure your own website and individual newsletter.
- My watch list
- My saved searches
- My saved topics
- My newsletter
Gas laws
The gas laws are a set of laws that describe the relationship between thermodynamic temperature (T), pressure (P) and volume (V) of gases. They are a loose collection of rules developed between the late Renaissance and early 19th century. Product highlightThree earlier gas laws:
were combined to form the combined gas law With the addition of Avogadro's law, this developed into the
where
(The law works with any consistent set of units, provided that the temperature scale starts at absolute zero, and the appropriate gas constant is used.) An equivalent formulation of this law is: where
These equations are exact only for an ideal gas, which is a mathematical model. However, they are good approximations for many gases under many circumstances. This law has the following important consequences:
Other gas laws of historical importance include:
See alsoReferences
|
| This article is licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License. It uses material from the Wikipedia article "Gas_laws". A list of authors is available in Wikipedia. |




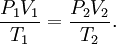
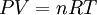 ,
,