Graphene heterostructures with black phosphorus, arsenic enable new infrared detectors
Sensors could replace any far-infrared and terahertz radiation detectors
Advertisement
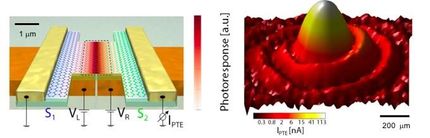
MIPT scientists and their colleagues from Japan and the U.S. have calculated the parameters of photodetectors comprised by layers of graphene and a combination of black phosphorus and black arsenic. These sensors are able to detect radiation with energy less than the band gap of the constituent layers without graphene. It is also easy to modify them in order to increase their sensitivity to the required wavelength of light. Such sensors could replace any far-infrared and terahertz radiation detectors.

Daria Sokol/MIPT Press Office
The new sensors will benefit many areas of science and technology. The far-infrared band is substantial both for household applications and for fundamental science. These waves are emitted by cosmic dust, whose study reveals the evolution of galaxies. Infrared light sensors are used in night vision equipment, remote controls, homing missiles, and heartbeat sensors. Terahertz radiation offers a less dangerous alternative to X-ray baggage scanners.
The researchers considered far-infrared interband photodetectors based on a graphene monolayer. The graphene was surrounded by layers made of black phosphorus and black arsenic in varying proportions. By changing the ratio of these substances, it is possible to shift the working range of the photodetector. The energies inaccessible to electrons in black phosphorus and arsenic are different. The detector operates by registering an electron or hole entering the conduction band of black phosphorus or arsenic following a transition between two energy bands of graphene. However, temperature effects cause infrared and terahertz sensors to detect signal even "in the dark," in the absence of radiation. The layered structures examined in the study turned out to experience a dark current much lower than in those used today.
"We calculated the parameters of the light-sensitive elements for far-infrared detection based on a graphene monolayer. Such devices can replace almost any far-infrared and terahertz radiation sensors used today. The decreased dark current and the high photosensitivity significantly improve the signal-to-noise ratio even for low-intensity radiation. By applying a carefully calibrated voltage, the working range of the detectors can be changed without affecting signal reception quality. Such sensors could enhance the performance of infrared telescopes. According to calculations, at high temperatures the detectors will produce a much cleaner signal than the detectors used now," adds Victor Ryzhii, the head of the 2D Materials and Nanodevices Laboratory.