First tri-continuous mesoporous Silica complex structure developed in Singapore
Technology useful for catalysis, separation and drug delivery
Advertisement
Singapore's Institute of Bioengineering and nanotechnology (IBN) has developed the first tri-continuous mesoporous material using a unique surfactant template. This completely new porous structure previously been predicted only mathematically.
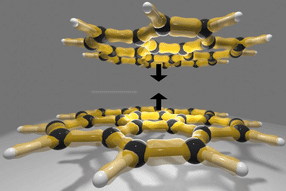
In the current Nature Chemistry, the IBN scientists report that this novel material, named IBN-9 after the research institute, is the first hexagonal nanoscale construct with 3 unconnected interwoven channels. It is by far the most complex mesoporous nanostructure to have been synthesized in real-life and represents a new class of mesoporous materials, which consist of pores of 2-50 nanometers in size.
Mesoporous silica has well-defined nanochannel structures that are formed over templates via self-assembly processes. Mesoporous silica materials have huge surface areas, making them ideal for use as catalysts to facilitate chemical reactions. Their uniform nanometersized pores allow them to separate molecules by size difference. Their pores may also be used to trap drug molecules for controlled drug release. Therefore, the ability to tailor the pore structure of mesoporous material is of fundamental importance for various chemical and biological applications.
"IBN-9 demonstrates that it is possible to create three interwoven but independent pore channel systems along with a unique nano-fiber morphology," said Jackie Y. Ying, Ph.D., who led this research.
"Such a mesostructure makes distinct diffusion rates in different directions possible. This property would be very attractive for gas separation and drug delivery systems" added Dr. Ying, Executive Director of IBN, which is part of Singapore's A*STAR (Agency for Science, Technology and Research).
There has been tremendous interest about tailoring mesoporous materials with unique pore structures and pore sizes. The most complex of these were the bi-continuous structures, which contain two unconnected interwoven channels. These materials are synthesized via self-assembly of silica around surfactant templates.
IBN researchers successfully synthesized the first tri-continuous mesoporous structure by using a specially designed surfactant template, N,N-dimethyl-L-phenylalanine. This surfactant has a unique tunable head-group as well as a long hydrocarbon tail that has variable levels of hydrophobic (water-repellent) qualities. By systematically changing the synthesis conditions using this surfactant, IBN researchers are able to achieve structures with increasing mean curvatures from the bi-continuous cubic IBN-6 to the tri-continuous 3D hexagonal IBN-9, and finally to the 2D hexagonal IBN-10. The structural complexity of IBN-9 and its sister materials opens the possibility of creating even more complex multi-continuous mesostructures.
Original publications: Y. Han et al.; "A Tri-Continuous Mesoporous Material, IBN-9, with a Silica Pore Wall Following a Hexagonal Minimal Surface," Nature Chemistry 2009
S. T. Hyde and G. E. Schröder; "Novel Surfactant Mesostructural Topologies: Between Lamellae and Columnar (Hexagonal) Forms"; Current Opinion in Colloid and Interface Science, 8 (2003) 5-14
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.

Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.