Researchers synthesize magnetic nanoparticles that could offer alternative to rare Earth magnets
Advertisement
A team of scientists at Virginia Commonwealth University has synthesized a powerful new magnetic material that could reduce the dependence of the United States and other nations on rare earth elements produced by China.
"The discovery opens the pathway to systematically improving the new material to outperform the current permanent magnets," said Shiv Khanna, Ph.D., a commonwealth professor in the Department of Physics in the College of Humanities and Sciences.
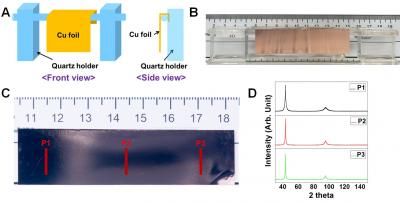
The new material consists of nanoparticles containing iron, cobalt and carbon atoms with a magnetic domain size of roughly 5 nanometers. It can store information up to 790 kelvins with thermal and time-stable, long-range magnetic order, which could have a potential impact for data storage application.
When collected in powders, the material exhibits magnetic properties that rival those of permanent magnets that generally contain rare earth elements. The need to generate powerful magnets without rare earth elements is a strategic national problem as nearly 70 to 80 percent of the current rare earth materials are produced in China.
The team's findings will appear in the article "Experimental evidence for the formation of CoFe2C phase with colossal magnetocrystalline-anisotropy," in Applied Physics Letters.
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.