A more energy-efficient catalytic process to produce olefins
Advertisement
Research at the University of Pittsburgh led to a more energy-efficient catalytic process to produce olefins, the building blocks for polymer production. The team's investigations could influence potential applications in diverse technology areas from green energy and sustainable chemistry to materials engineering and catalysis.

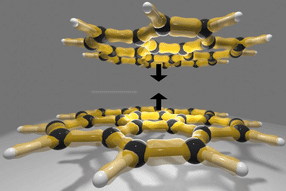
Inside front cover of Catalysis Science & Technology. Catal. Sci. Technol., 2017, 7, 1974-1974 - Reproduced by permission of The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Giannis Mpourmpakis/Computer-Aided Nano and Energy Lab
"Carboranes are one of the strongest known acids, but little is known about how these molecular catalysts can dehydrate biomass-derived alcohols," Dr. Mpourmpakis explained. "Our computational research not only detailed the mechanism under which alcohols dehydrate on these catalysts, but most importantly we developed linear relationships between the energy input needed to observe dehydration of alcohols and the alcohol characteristics."
According to the paper, "these obtained relationships are especially relevant to the field of solid acid catalysis, a widely studied area with a vast range of industrial applications, including the formation of olefins (polymer building blocks) from biomass-derived alcohols as well as fuels and chemicals from sugars and polyols." The group's research focused on primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols, and revealed the slope of linear relationships depending on the reaction mechanism.
"This research is important because now experimentalists have a way to identify the reaction followed when different alcohols dehydrate," Mpourmpakis said. "Because this process involves biomass-based production of polymers, we can potentially create a more sustainable and energy-efficient process."
Original publication
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.

Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.