Divide and conquer: A key to creating better medicines with fewer side effects
Advertisement
A new study by Professors Yossi Paltiel of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem and Ron Naaman from the Weizmann Institute of Science describes a breakthrough technology with the power to create drugs with fewer unwanted side effects.
Chiral molecule
Palitel and Naaman
Chemical compounds are made up of molecules. The most important molecules in biology are chiral molecules. "Chiral," the Greek word for "hand," describes molecules that look almost exactly alike and contain the same number of atoms but are mirror images of one another--meaning some are "left-handed" and others are "right-handed". This different "handedness" is crucial and yields different biological effects.
Though a crucial step for drug safety, the separation of chiral molecules into their right- and left- handed components is an expensive process and demands a tailor-made approach for each type of molecule. Now, however, following a decade of collaborative research, Paltiel and Naaman have discovered a uniform, generic method that will enable pharmaceutical and chemical manufactures to easily and cheaply separate right from left chiral molecules.
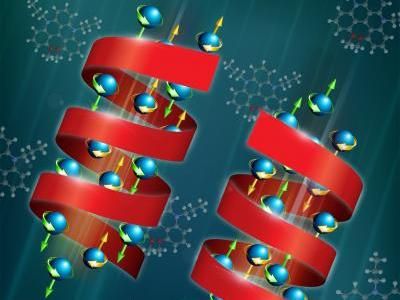
Their method relies on magnets. Chiral molecules interact with a magnetic substrate and line up according to the direction of their handedness --"left" molecules interact better with one pole of the magnet, and "right" molecules with the other one. This technology will allow chemical manufacturers to keep the "good" molecules and to discard the "bad" ones that cause harmful or unwanted side effects.
"Our finding has great practical importance", shared Prof. Naaman. "It will usher in an era of better, safer drugs, and more environmentally-friendly pesticides".
While popular drugs, such as Ritalin and Cipramil, are sold in their chirally-pure (i.e., separated) forms, many generic medications are not. Currently only 13% of chiral drugs are separated even though the FDA recommends that all chiral drugs be separated. Further, in the field of agrochemicals, chirally-pure pesticides and fertilizers require smaller doses and cause less environmental contamination than their unseparated counterparts.
With these statistics in mind, Paltiel and Naaman's simple and cost effective chiral separation technique has the ability to produce better medical and agricultural products, including medicines, food ingredients, dietary supplements and pesticides.
"We are now transforming our science into practice, with the help of Weizmann's and the Hebrew University's technology transfer companies. Placing better medical and environmental products on the market is a win-win for industry and for patients," concluded Paltiel.
Original publication
Banerjee-Ghosh, Koyel and Ben Dor, Oren and Tassinari, Francesco and Capua, Eyal and Yochelis, Shira and Capua, Amir and Yang, See-Hun and Parkin, Stuart S. P. and Sarkar, Soumyajit and Kronik, Leeor and Baczewski, Lech Tomasz and Naaman, Ron and Paltiel, Yossi; "Separation of enantiomers by their enantiospecific interaction with achiral magnetic substrates"; Science; 2018