New synthetic route for biofuel production
Compared to previous methods, the team has achieved a high yield and selectivity under less aggressive reaction conditions
Advertisement
A German-Chinese research team has found a new synthetic route to produce biofuel from biomass. The chemists converted the substance 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) produced from biomass into 2,5-dimethylfuran (DMF), which could be suitable as a biofuel. Compared to previous methods, they achieved a higher yield and selectivity under milder reaction conditions. The team led by Dr. Baoxiang Peng and Professor Martin Muhler from the Laboratory of Industrial Chemistry at Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) and the group led by Professor Christof Hättig from the RUB Chair for Theoretical Chemistry described the method together with colleagues from Changzhou, China, in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
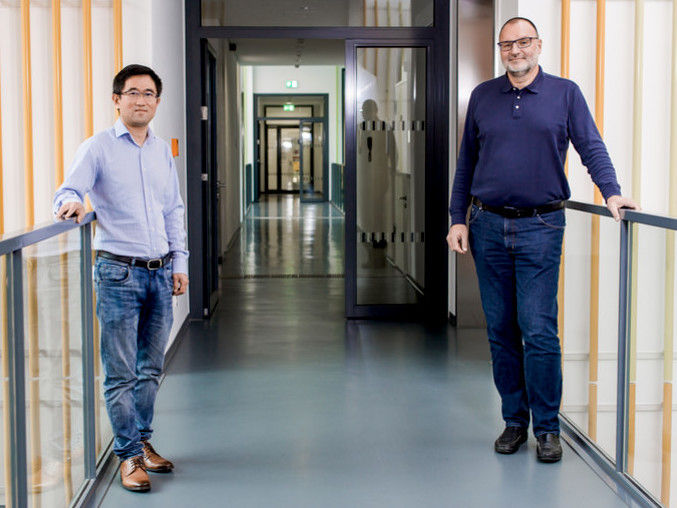

The Bochum-based catalysis team: Baoxiang Peng (left) and Martin Muhler
© RUB, Rohlf
The work was part of the German-Chinese research cooperation “Novel Functional Materials for Sustainable Chemistry”, which is supported by the German Research Foundation.
Better fuel than ethanol
“DMF would be well-suited as a biofuel, as it has a higher octane number than ethanol, a better energy intensity and an ideal boiling point of 92 to 94 degree Celsius,” explains Baoxiang Peng. Although the conversion from HMF into DMF has been researched intensively, there are several hurdles. DMF production requires relatively harsh reaction conditions, such as high hydrogen pressure, and often only creates a small quantity of the desired product, while also forming unwanted by-products. Researchers are thus looking for new ways to efficiently trigger the reaction under milder conditions. This was achieved in the current work.
Formic acid as the key to success
The team carried out the reaction in the presence of formic acid and hydrogen. Palladium nanoparticles were used as a catalyst. In doing so, the chemists achieved a five-times larger reaction rate than those reported with previous methods. The addition of formic acid, in particular, played a crucial role in creating favourable reaction conditions, as shown by the researchers in their detailed investigations.
They performed the reaction with various additives and compared the yield and selectivity, which were best in the presence of formic acid. The substance facilitates a faster reaction pathway and also prevents the occurrence of unwanted side reactions.
Original publication
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.

Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.