Connecting the (Nano)dots
Big-picture thinking can advance nanoparticle manufacturing
Advertisement
Nanoparticle manufacturing, the production of material units less than 100 nanometers in size (100,000 times smaller than a marble), is proving the adage that “good things come in small packages.” Today’s engineered nanoparticles are integral components of everything from the quantum dot nanocrystals coloring the brilliant displays of state-of-the-art televisions to the miniscule bits of silver helping bandages protect against infection. However, commercial ventures seeking to profit from these tiny building blocks face quality control issues that, if unaddressed, can reduce efficiency, increase production costs and limit commercial impact of the products that incorporate them.

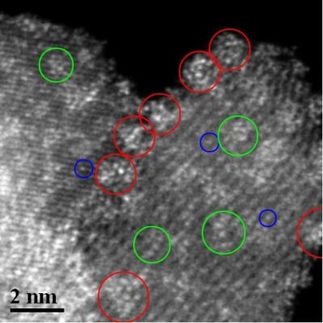
Electron micrograph showing gallium arsenide nanoparticles of varying shapes and sizes. Such heterogeneity can increase costs and limit profits when making nanoparticles into products. A new NIST study recommends that researchers, manufacturers and administrators work together to solve this, and other common problems, in nanoparticle manufacturing.
A. Demotiere, E. Shevchenko/Argonne National Laboratory
To help overcome these obstacles, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the nonprofit World Technology Evaluation Center (WTEC) advocate that nanoparticle researchers, manufacturers and administrators “connect the dots” by considering their shared challenges broadly and tackling them collectively rather than individually. This includes transferring knowledge across disciplines, coordinating actions between organizations and sharing resources to facilitate solutions.
“We looked at the big picture of nanoparticle manufacturing to identify problems that are common for different materials, processes and applications,” said NIST physical scientist Samuel Stavis, lead author of the paper. “Solving these problems could advance the entire enterprise.”
The new paper provides a framework to better understand these issues. It is the culmination of a study initiated by a workshop organized by NIST that focused on the fundamental challenge of reducing or mitigating heterogeneity, the inadvertent variations in nanoparticle size, shape and other characteristics that occur during their manufacture.
“Heterogeneity can have significant consequences in nanoparticle manufacturing,” said NIST chemical engineer and co-author Jeffrey Fagan.
In their paper, the authors noted that the most profitable innovations in nanoparticle manufacturing minimize heterogeneity during the early stages of the operation, reducing the need for subsequent processing. This decreases waste, simplifies characterization and improves the integration of nanoparticles into products, all of which save money.
The authors illustrated the point by comparing the production of gold nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes. For gold, they stated, the initial synthesis costs can be high, but the similarity of the nanoparticles produced requires less purification and characterization. Therefore, they can be made into a variety of products, such as sensors, at relatively low costs.
In contrast, the more heterogeneous carbon nanotubes are less expensive to synthesize but require more processing to yield those with desired properties. The added costs during manufacturing currently make nanotubes only practical for high-value applications such as digital logic devices.
“Although these nanoparticles and their end products are very different, the stakeholders in their manufacture can learn much from each other’s best practices,” said NIST materials scientist and co-author J. Alexander Liddle. “By sharing knowledge, they might be able to improve both seemingly disparate operations.”
Finding ways like this to connect the dots, the authors said, is critically important for new ventures seeking to transfer nanoparticle technologies from laboratory to market.
“Nanoparticle manufacturing can become so costly that funding expires before the end product can be commercialized,” said WTEC nanotechnology consultant and co-author Michael Stopa. “In our paper, we outlined several opportunities for improving the odds that new ventures will survive their journeys through this technology transfer ‘valley of death.’”
Finally, the authors considered how manufacturing challenges and innovations are affecting the ever-growing number of applications for nanoparticles, including those in the areas of electronics, energy, health care and materials.