Robust and flexible to synthetic methane
New reactor concept for methanation: Direct feed into the gas grid
Advertisement
Synthetic energy carriers are carbon-neutral and make renewable energy transportable and storable in the long term. Synthetically produced methane is one of them. The problem: The production involves rather high energy losses; moreover, existing processes require the methane to be purified. To change this, Empa researchers have developed a new, optimized reactor concept for methanation.
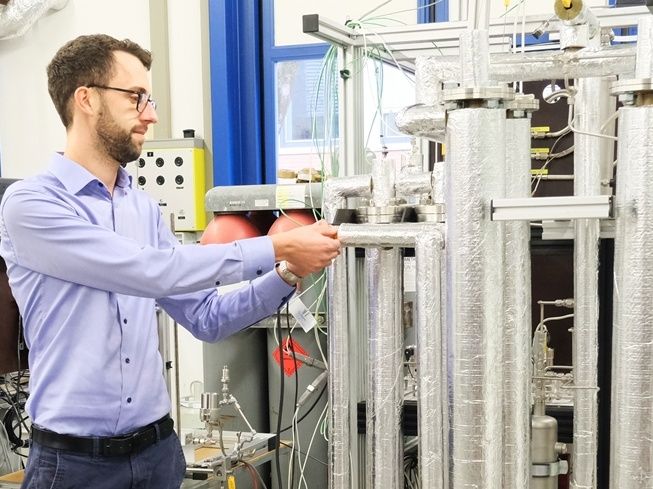

The findings from the new reactor concept can be implemented for large-scale plant: Florian Kiefer, project manager for sorption-enhanced methanation, next to the test plant.
Empa
A successful energy transition requires energy sources that are climate-friendly; this means: as few CO2 emissions as possible – ideally none at all – during production and use. Synthetic energy carriers – i.e. those that are obtained from renewable energy through chemical conversion processes – are one of the most promising options. The use of such energy carriers only produces as much CO2 as was previously removed from the atmosphere for their production.
Artificially produced methane falls into this category. "Synthetic gas offers enormous potential if it is produced from atmospheric CO2 and renewably generated hydrogen," explains Christian Bach, head of Empa's Automotive Powertrain Technologies lab. "However, for hydrogen production you need a lot of water as well as renewable electricity. In our mobility demonstrator move, we thus want to extract not only CO2 but also the water for hydrogen production directly from the atmosphere with the help of a CO2 collector from the ETH spin-off Climeworks." In future, such concepts could be implemented in desert regions lacking liquid water supplies.
However, the production of synthetic methane from hydrogen and CO2 – so-called methanation– has its pitfalls. This is because methane produced by such a catalytic process still contains hydrogen, which prevents it from being fed directly into the gas grid. Empa researchers Florian Kiefer, Marin Nikolic, Andreas Borgschulte and Panayotis Dimopoulos Eggenschwiler have therefore developed a new reactor concept, in which the formation of hydrogen on the product side is prevented. This leads to a simpler process control and a better suitability for dynamic operation, e.g. for coupling with unsteadily available renewable energies. The project is supported by the Canton of Zurich, Avenergy Suisse, Migros, Lidl Switzerland, Armasuisse, Swisspower and the ETH Board.
Direct feed into the gas grid thanks to water adsorption
At move, the hydrogen-free methane is produced by a process called sorption-enhanced methanation. The idea: The water produced during the reaction is continuously adsorbed on a porous catalyst support during methanation. Continuous removal of water results in just methane as a product – in pure form – eliminating the need to purify the (previous) product mixture. At the end of the reaction, the catalyst support material is dried again by lowering the pressure – and is ready for the next reaction cycle. "This process is more flexible and stable than previous processes, but it also has some potential for energy savings because we can run it at a lower pressure and do without hydrogen separation and recirculation. However, a precise assessment of the energy efficiency will only be possible once the demonstrator is in full operation," explains Florian Kiefer, project leader for sorption-enhanced methanation at move.
From laboratory to industrial plant
Florian Kiefer and his team spent around three years developing a new reactor concept with zeolite pellets that act as a porous catalyst carrier and simultaneously adsorb the water produced during the methanation reaction. The focus was also on upscaling the process – in other words, a concept for how this process can be implemented for large-scale plants. To this end, Empa collaborated with various partners from industry. The regeneration time, i.e. the time needed to dry the reactor, is crucial for the reactor design and for process planning. To ensure continuous methane production, at least two reactors must operate alternately. Heat management is also crucial for the drying of the reactors, either by removing heat from the reactor or by storing heat internally in the catalyst bed. Kiefer's team has already filed a patent in this area.