Graphene under pressure
Advertisement
Small balloons made from one-atom-thick material graphene can withstand enormous pressures, much higher than those at the bottom of the deepest ocean, scientists at the University of Manchester report.
This is due to graphene's incredible strength - 200 times stronger than steel.
The graphene balloons routinely form when placing graphene on flat substrates and are usually considered a nuisance and therefore ignored. The Manchester researchers, led by Professor Irina Grigorieva, took a closer look at the nano-bubbles and revealed their fascinating properties.
These bubbles could be created intentionally to make tiny pressure machines capable of withstanding enormous pressures. This could be a significant step towards rapidly detecting how molecules react under extreme pressure.
The scientists found that the shape and dimensions of the nano-bubbles provide straightforward information about both graphene's elastic strength and its interaction with the underlying substrate.
The researchers found such balloons can also be created with other two-dimensional crystals such as single layers of molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) or boron nitride.
They were able to directly measure the pressure exerted by graphene on a material trapped inside the balloons, or vice versa.
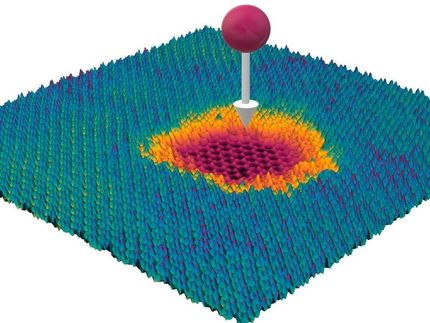
To do this, the team indented bubbles made by graphene, monolayer MoS2 and monolayer boron nitride using a tip of an atomic force microscope and measured the force that was necessary to make a dent of a certain size.
These measurements revealed that graphene enclosing bubbles of a micron size creates pressures as high as 200 megapascals, or 2,000 atmospheres. Even higher pressures are expected for smaller bubbles.
Ekaterina Khestanova, a PhD student who carried out the experiments, said: "Such pressures are enough to modify the properties of a material trapped inside the bubbles and, for example, can force crystallization of a liquid well above its normal freezing temperature'.
Sir Andre Geim, a co-author of the paper, added: "Those balloons are ubiquitous. One can now start thinking about creating them intentionally to change enclosed materials or study the properties of atomically thin membranes under high strain and pressure."
Original publication
E. Khestanova, F. Guinea, L. Fumagalli, A. K. Geim, and I. V. Grigorieva; "Universal shape and pressure inside bubbles appearing in van der Waals Heterostructures"; Nature Comm.; 2016