Breaking the chain
Catalyzing a green future for chemistry
Advertisement
The fight against climate change is a call-to-arms for industry. We currently rely on fossil fuels, a major source of the greenhouse gas CO2 , not only for energy but also to create chemicals for manufacturing. To ween our economies off this dependency, we must find a new source of "green" raw materials so that factories and laboratories can run without producing and emitting CO2.
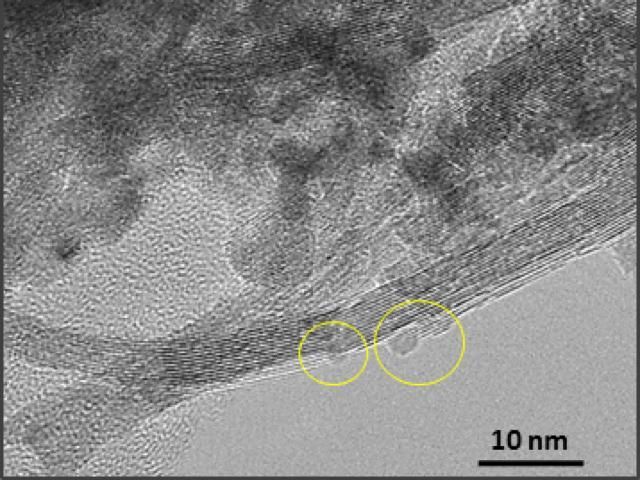
This is a TEM image of CeO2-supported ruthenium nanoparticles catalyst. Yellow circles show Ru nanoparticles.
Osaka University
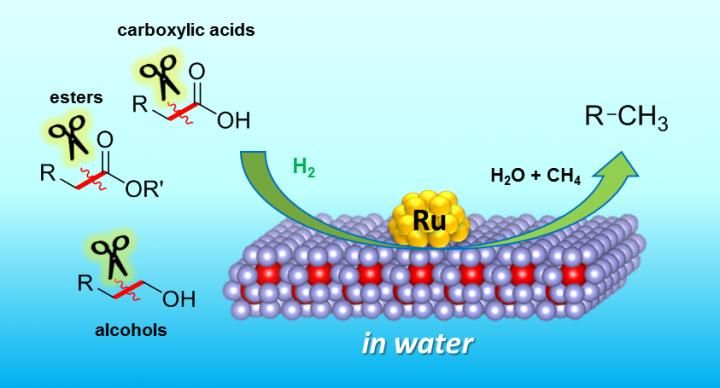
These are selective C-C bond cleavages of biogenic chemicals catalyzed by the CeO2-supported ruthenium nanoparticle catalyst.
Osaka University
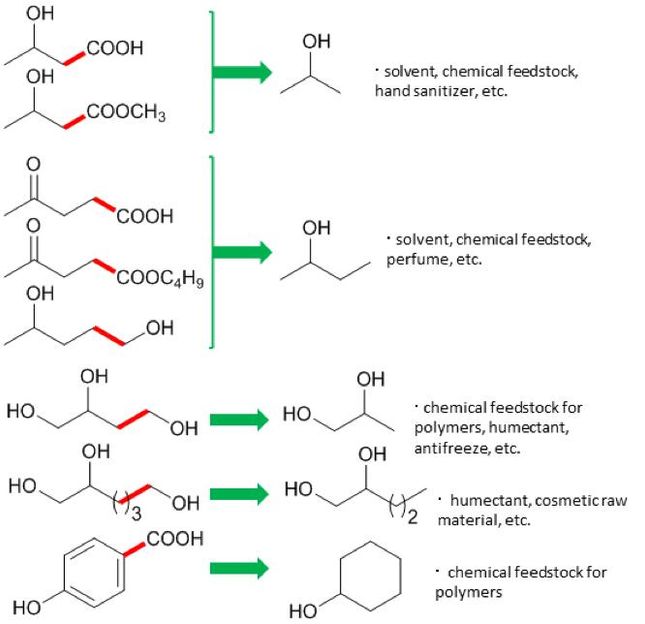
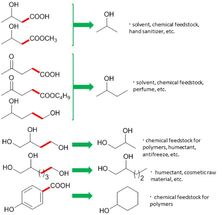
These are the new synthetic routes for valuable chemicals using the CeO2-supported ruthenium nanoparticle catalyst.
Osaka University

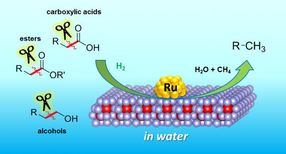
Now, a research team at Osaka University has discovered how to create valuable chemicals from clean sources. They used biomass, essentially waste from plant materials. Biomass is rich in organic molecules - long chains of carbon atoms attached to oxygen. Existing methods can break the carbon-oxygen bonds in these molecules to create, for example, raw materials for plastics. However, breaking the carbon-carbon bonds, in order to shorten the molecular chains, is harder; extreme temperatures are needed, and often yield unwanted products.
The method developed at Osaka is based on a new catalyst. Catalysts allow reactions to occur, without being consumed themselves. They are often based on metals, and the new example is no exception - it consists of atomically small particles of ruthenium, a metal related to iron, sitting on a material called cerium oxide.
After creating their catalyst, the researchers tested it on levulinic acid (LA) from biomass. LA was reacted to break C-C bond at 150 degrees Celsius - hot for some, but mild by industrial standards. The reaction product was 2-butanol, an important chemical for manufacturing solvents. "This is the first time that 2-butanol has been made in this green way, using LA," study first author Tomoo Mizugaki explains. "Traditionally, it is made from butene, which comes from highly polluting oil refineries."
Buoyed by this, the team tested their catalyst on other biomass chemicals. A range of valuable products was obtained. Crucially, the reactions always broke carbon-carbon bonds. This allowed them to produce, for example, cyclohexanol, an important chemical in the manufacture of nylon.
X-ray and microscope studies confirmed that the combination of ruthenium, cerium oxide and water was vital for the reaction to occur. The new catalyst therefore fills an important gap in the chemist's toolbox of reactions.
"We hope this method helps all sectors of industry obtain raw materials from non-fossil sources," corresponding author Kiyotomi Kaneda says. "We need a radical change in thinking, so that bio-derived chemicals are considered as primary options in manufacturing."