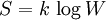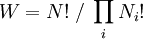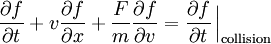To use all functions of this page, please activate cookies in your browser.
my.chemeurope.com
With an accout for my.chemeurope.com you can always see everything at a glance – and you can configure your own website and individual newsletter.
- My watch list
- My saved searches
- My saved topics
- My newsletter
Ludwig Boltzmann
Ludwig Eduard Boltzmann (February 20, 1844 – September 5, 1906) was an Austrian physicist famous for his founding contributions in the fields of statistical mechanics and statistical thermodynamics. He was one of the most important advocates for atomic theory when that scientific model was still highly controversial. Product highlight
BiographyChildhood and educationBoltzmann was born in Vienna, then capital of the Austrian Empire. His father, Ludwig George Boltzmann, was a tax official. His grandfather, who had moved to Vienna from Berlin, was a clock manufacturer, and Boltzmann’s mother, Katharina Pauernfeind, was originally from Salzburg. He received his primary education from a private tutor at the home of his parents. Boltzmann attended high school in Linz, Upper Austria. At age 15, Boltzmann lost his father. Boltzmann studied physics at the University of Vienna, starting in 1863. Among his teachers were Josef Loschmidt, Joseph Stefan, Andreas von Ettingshausen and Jozef Petzval. Boltzmann received his PhD degree in 1866 working under the supervision of Stefan; his dissertation was on kinetic theory of gases. In 1867 he became a Privatdozent (lecturer). After obtaining his doctorate degree, Boltzmann worked two more years as Stefan’s assistant. It was Stefan who introduced Boltzmann to Maxwell's work. Academic careerIn 1869, at age 25, he was appointed full Professor of Mathematical Physics at the University of Graz in the province of Styria. In 1869 he spent several months in Heidelberg working with Robert Bunsen and Leo Königsberger and then in 1871 he was with Gustav Kirchhoff and Hermann von Helmholtz in Berlin. In 1873 Boltzmann joined the University of Vienna as Professor of Mathematics and there he stayed until 1876. In 1872, long before women were admitted to Austrian universities, he met Henriette von Aigentler, an aspiring teacher of mathematics and physics in Graz. She was refused permission to unofficially audit lectures, and Boltzmann advised her to appeal; she did, successfully. On July 17, 1876 Ludwig Boltzmann married Henriette von Aigentler; they had three daughters and two sons. Boltzmann went back to Graz to take up the chair of Experimental Physics. Among his students in Graz were Svante Arrhenius, and Walther Nernst. He spent 14 happy years in Graz and it was there that he developed his statistical concept of nature. In 1885 he became a member of the Imperial Austrian Academy of Sciences and in 1887 he became the President of the University of Graz. Boltzmann was appointed to the Chair of Theoretical Physics at the University of Munich in Bavaria, Germany in 1890. In 1893, Boltzmann succeeded his teacher Joseph Stefan as Professor of Theoretical Physics at the University of Vienna. Final yearsHowever, Boltzmann did not get along with some of his colleagues in Vienna, particularly Ernst Mach, who became a professor of philosophy and history of sciences in 1895. Thus in 1900 Boltzmann went to the University of Leipzig, on the invitation of Wilhelm Ostwald. After the retirement of Mach due to bad health, Boltzmann came back to Vienna in 1902. His students included Karl Przibram, Paul Ehrenfest and Lise Meitner.
In Vienna, Boltzmann not only taught physics but also lectured on philosophy. Boltzmann’s lectures on natural philosophy were very popular, and received a considerable attention at that time. His first lecture was an enormous success. Even though the largest lecture hall had been chosen for it, the people stood all the way down the staircase. Because of the great successes of Boltzmann’s philosophical lectures, the Emperor invited him for a reception at the Palace. Boltzmann was subject to rapid alternation of depressed moods with elevated, expansive or irritable moods. He himself jestingly attributed his rapid swings in temperament to the fact that he was born during the night between Mardi Gras and Ash Wednesday;[citation needed] he had, almost certainly, bipolar disorder [2]. Meitner relates that those who were close to Boltzmann were aware of his bouts of severe depression and his suicide attempts. On September 5, 1906, while on a summer vacation in Duino, near Trieste, Boltzmann committed suicide during an attack of depression. He is buried in Vienna and his tombstone reads S=k*logW. PhysicsBoltzmann's most important scientific contributions were in kinetic theory, including the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution for molecular speeds in a gas. In addition, Maxwell-Boltzmann statistics and the Boltzmann distribution over energies remain the foundations of classical statistical mechanics. They are applicable to the many phenomena that do not require quantum statistics and provide a remarkable insight into the meaning of temperature. Much of the physics establishment did not share his belief in the reality of atoms and molecules — a belief shared, however, by Maxwell in Scotland and Gibbs in the United States; and by most chemists since the discoveries of John Dalton in 1808. He had a long-running dispute with the editor of the preeminent German physics journal of his day, who refused to let Boltzmann refer to atoms and molecules as anything other than convenient theoretical constructs. Only a couple of years after Boltzmann's death, Perrin's studies of colloidal suspensions (1908-1909) confirmed the values of Avogadro's number and Boltzmann's constant, and convinced the world that the tiny particles really exist. To quote Planck, "The logarithmic connection between entropy and probability was first stated by L. Boltzmann in his kinetic theory of gases"[1]This famous formula for entropy S is[2] [3] where k = 1.3806505(24) × 10−23 J K−1 is Boltzmann's constant, and the logarithm is taken to the natural base e. W is the Wahrscheinlichkeit, the frequency of occurrence of a macrostate[4] or, more precisely, the number of possible microstates corresponding to the macroscopic state of a system — number of (unobservable) "ways" the (observable) thermodynamic state of a system can be realized by assigning different positions and momenta to the various molecules. Boltzmann’s paradigm was an ideal gas of N identical particles, of which Ni are in the i-th microscopic condition (range) of position and momentum. W can be counted using the formula for permutations where i ranges over all possible molecular conditions. (! denotes factorial.) The "correction" in the denominator is because identical particles in the same condition are indistinguishable. W is called the "thermodynamic probability" since it is an integer greater than one, while mathematical probabilities are always numbers between zero and one. The equation for S is engraved on Boltzmann's tombstone at the Vienna Zentralfriedhof — his second grave. The Boltzmann equation
The Boltzmann equation was developed to describe the dynamics of an ideal gas. where f represents the distribution function of single-particle position and momentum at a given time (see the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution), F is a force, m is the mass of a particle, t is the time and v is an average velocity of particles. This equation describes the temporal and spatial variation of the probability distribution for the position and momentum of a density distribution of a cloud of points in single-particle phase space. (See Hamiltonian mechanics.) The first term on the left-hand side represents the explicit time variation of the distribution function, while the second term gives the spatial variation, and the third term describes the effect of any force acting on the particles. The right-hand side of the equation represents the effect of collisions.
In principle, the above equation completely describes the dynamics of an ensemble of gas particles, given appropriate boundary conditions. This first-order differential equation has a deceptively simple appearance, since f can represent an arbitrary single-particle distribution function. Also, the force acting on the particles depends directly on the velocity distribution function f. The Boltzmann equation is notoriously difficult to integrate. David Hilbert spent years trying to solve it without any real success. The form of the collision term assumed by Boltzmann was approximate. However for an ideal gas the standard Chapman-Enskog solution of the Boltzmann equation is highly accurate. It is expected to lead to incorrect results for an ideal gas only under shock wave conditions. Boltzmann tried for many years to "prove" the second law of thermodynamics using his gas-dynamical equation — his famous H-theorem. However the key assumption he made in formulating the collision term was "molecular chaos", an assumption which breaks time-reversal symmetry as is necessary for anything which could imply the second law. It was from the probabilistic assumption alone that Boltzmann's apparent success emanated, so his long dispute with Loschmidt and others over Loschmidt's paradox ultimately ended in his failure. Finally, in the 1970s E.G.D. Cohen and J.R. Dorfman proved that a systematic (power series) extension of the Boltzmann equation to high densities is mathematically impossible. Consequently nonequilibrium statistical mechanics for dense gases and liquids focuses on the Green-Kubo relations, the fluctuation theorem, and other approaches instead. Energetics of evolutionBoltzmann's views played an essential role in the development of energetics, the scientific study of energy flows under transformation. In 1922, for example, Alfred J. Lotka referred to Boltzmann as one of the first proponents of the proposition that available energy, also called exergy, can be understood as the fundamental object under contention in the biological, or life-struggle and therefore also in the evolution of the organic world.[5] Lotka interpreted Boltzmann's view to imply that available energy could be the central concept that unified physics and biology as a quantitative physical principle of evolution. In the forward to Boltzmann's Theoretical Physics and Philosophical Problems, S.R. de Groot noted that
Howard T. Odum later sought to develop these views when looking at the evolution of ecological systems, and suggested that the maximum power principle was an example of Darwin's law of natural selection. Significant contributions1872 - Boltzmann equation; H-theorem 1877 - Boltzmann distribution; relationship between thermodynamic entropy and probability. 1884 - Derivation of the Stefan-Boltzmann law EvaluationsClosely associated with a particular interpretation of the second law of thermodynamics, he is also credited in some quarters with anticipating quantum mechanics. For detailed and technically informed account of Boltzmann's contributions to statistical mechanics consult the article by E.G.D. Cohen. See also
References
Further reading
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This article is licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License. It uses material from the Wikipedia article "Ludwig_Boltzmann". A list of authors is available in Wikipedia. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||