New method converts carbon dioxide to methane at low temperatures
Advertisement
A new method developed by a team of Waseda University scientists led by Professor Yasushi Sekine may contribute to reducing the use of fossil fuels and help prevent global warming in the long-run.
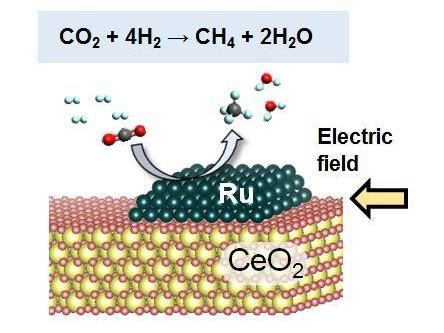
Hydrogenation of CO2 to CH4
Sekine Laboratory, Waseda University
The conversion of carbon dioxide to valuable chemicals such as methane has drawn great attention for use in supporting carbon capture and utilization. Especially, methane can be used not only as fuel but also as a hydrogen carrier, transporting town gas to existing infrastructure. For instance, some plants in Germany have already been launched based on the Power to Gas concept, which allows energy from electricity to be stored and transported in the form of compressed gas.
"To recycle carbon dioxide into methane, an established industrial method involves the reaction of hydrogen and carbon dioxide using a ruthenium-based catalyst at temperatures of 300 to 400 degrees Celsius, but this method limited how much and when methane could be produced since it requires such high temperature," Sekine says. "Additionally, operation at low temperatures was demonstrated to be favorable to improve carbon dioxide conversion and increase the amount of methane produced."
In this newly-developed method reported in Chemistry Letters, carbon dioxide can be converted into methane more efficiently and quickly in the 100 degrees Celsius range.
"This method involves a reaction of nanoparticles called cerium oxide with carbon dioxide in presence of ruthenium catalyst with an electric field," explains Sekine. "The results show that the catalyst exhibited high and stable catalytic activity for converting carbon dioxide to methane through hydrogenation with the electric field."
With this novel method, methane could be produced from carbon dioxide collected from the atmosphere, possibly enabling an unlimited amount of methane production by recycling carbon dioxide from the atmosphere released from factories into valuable energy resources.